Consider the types of current and their impact on charging
Buying an electric vehicle without knowing and understanding the current used at the charging station can harm your needs. Let’s see how AC and DC affect electric car charging.
AC connectors
DC connectors
AC / DC Charging
The most important thing to consider before buying any vehicle is its fuel. So most of the questions are raised about its charging mechanism. There are many myths and ambiguities about electric cars running on electricity.
What are the different types of charging stations? And how fast does an electric car charge?
Alternating Current (AC)
Alternating current (AC) is transmitted via power lines, and there are 230V and 50 Hz in a standard electrical outlet in most parts of (as is in Pakistan UK, Europe, Australia, and most of Asia and Africa). Electric current is produced as alternating and it can be transmitted without much loss and over longer distances than it.
AC Charging
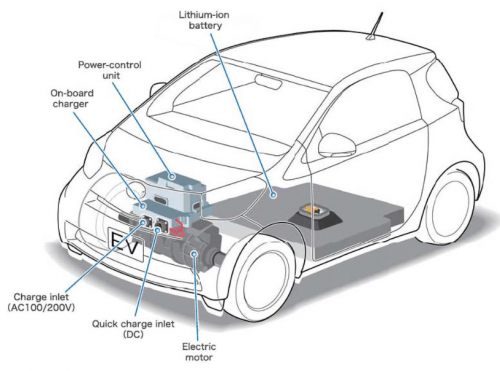
When charging an electric car with alternating current, the car’s on-board system (also called the on-board charger) is used and it takes care of the conversion of outlet current into battery current. It, therefore, receives alternating current (AC) and converts it into direct current (DC), which is then sent to the car battery.
The main advantage of AC stations is that they are affordable. They are cheaper than DC charging stations with the same efficiency. Another advantage they have is that they are very versatile. They are significantly smaller and their installation is easier. Thanks to their features, AC charging stations are also suitable for home installation and night charging.
AC Charging Station
The disadvantage of AC charging stations is that they are slower. However, the technology is still improving and today AC charging stations can provide up to 22 kWh of charging power. If the battery of the electric car has a capacity of 21 kWh, it can be fully charged in about an hour.
When charging with AC stations, the electrical grid is connected to the onboard charger.
Direct Current (DC)
The DC fast charger continues regardless of the limitations of the onboard charger. The charging speed can be greatly increased. Charging times depend on battery size, dispenser output, and other factors. Most vehicles can receive an 80% charge in 50 minutes using a DC charger.
DC Charging
A DC charging station is technologically more complex and often more expensive than an AC charging station. Unlike AC chargers, a DC charger has a converter inside the charger itself. can feed power directly to the car’s battery.
DC Charging Station
DC chargers can provide a higher power output than most residential AC chargers. This capability facilitates fast charging.
DC (Direct Current) fast charging offers several advantages for electric vehicles (EVs) over AC (Alternating Current) charging:
Charging speed: DC fast charging is significantly faster than AC charging. Depending on the power of the vehicle and charger, it can provide high power directly to the EV’s battery, allowing fast charging, often reaching 80% capacity in about 30-60 minutes.
However, while DC fast charging is convenient and fast, it may not be the most efficient way to charge every day. Regular use of fast charging, especially high-power DC fast charging, can potentially degrade the battery over time faster than slow AC charging. Therefore, a balance between fast charging and slow, overnight charging can be ideal to preserve battery health while ensuring the convenience of fast charging when needed.