It is a store of energy that contains the energy that will be used to drive a car, heat and cool, and all other lights and accessories. Typically, batteries use direct current electricity which must be converted to AC, or alternating current, before being used in an electric motor. Sometimes, you will find motors with direct current, but these are not uncommon in large-scale electric vehicles. DC charging is faster because it charges the batteries directly.
2- A power inverter.
When an EV has AC motors, it is necessary to convert the energy from the battery to use. The inverter also works when the car is using a regenerative brake that converts the alternating current generated by the electric motors into direct current to be stored in the battery.
3- An electric motor.
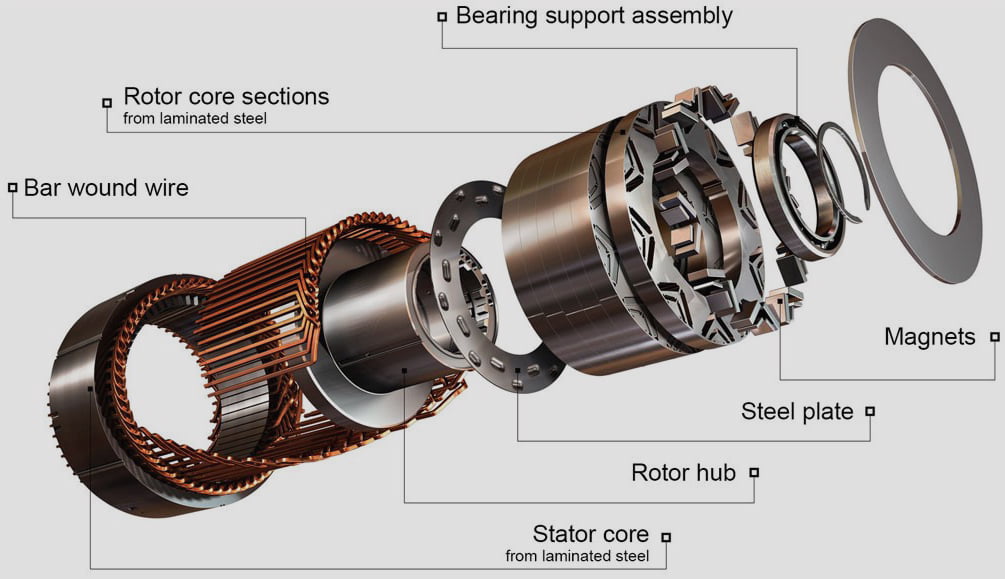
The component of an electric vehicle that converts electrical energy from a battery into circulation that can be used to move a vehicle. There are many types of electric motors and although the basic technology has not changed in the last 100 years, the design and performance of the motor have improved a lot
4- On-board battery charger.
Most EVs have a car battery charger for Level 1 or Level 2 charging. This is AC 4-charging, not DC fast charging. The charger is available to limit the total amount of electricity flowing into the battery to prevent damage to the battery or the electrical circuit in which the charger is inserted.
5- Battery Management System
BMS – Manages the flow of electricity inside and outside the battery to protect the battery and extend its life. Each EV will have a BMS designed specifically for the car battery. Thus, it can be very difficult to modify the battery or insert the battery if the BMS is not replaced to compensate.
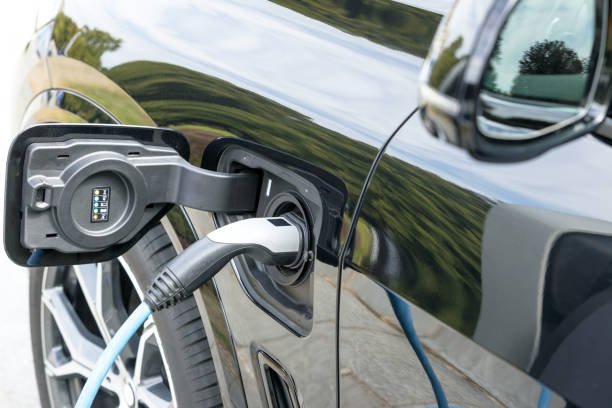
6- Charging port.
Like the access port for the gas tank in an internal combustion engine car, the charge port is where energy enters the ca




normal information
To be honest this meathead is quite the loser.